Pyrolysis is an innovative and environmentally friendly technology that plays a crucial role in waste management and resource recovery. It involves the thermal decomposition of organic materials at high temperatures in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the production of valuable products like biofuels, biochar, and syngas, while simultaneously reducing waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
Process Overview
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that breaks down organic materials such as biomass, plastics, rubber, and organic waste into their constituent elements and compounds through the application of heat. Unlike combustion, which requires oxygen and leads to the release of carbon dioxide, pyrolysis occurs in an oxygen-deprived environment, minimizing emissions and promoting sustainable waste management.

Key Steps
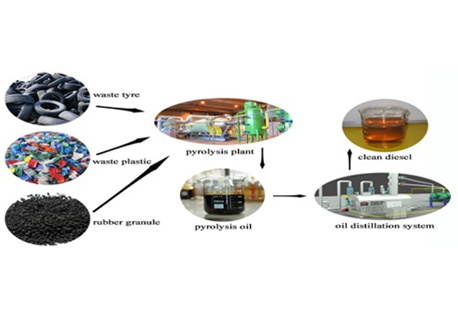
- Feedstock Preparation: The organic material, often referred to as feedstock, is first sorted and prepared for processing. This can include shredding, chipping, or sizing the material to ensure uniform heating.
- Pyrolysis Reactor: The prepared feedstock is then fed into a pyrolysis reactor, which is typically a high-temperature vessel or chamber. The temperature inside the reactor can range from 400°C to 800°C or higher, depending on the specific application and feedstock.
- Heating and Decomposition: As the feedstock is heated in the absence of oxygen, it undergoes thermal decomposition. This process breaks down the organic compounds into valuable products, including bio-oil, syngas (a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide), and solid residue known as biochar.
- Product Collection: The resulting products are collected and separated. Bio-oil can be further refined and used as a renewable fuel source or chemical feedstock. Syngas can be burned for energy generation or used in various industrial processes. Biochar is often used as a soil conditioner to enhance agricultural productivity.
Environmental Benefits
Pyrolysis technology offers several environmental advantages:
- It reduces the volume of waste going to landfills and incinerators.
- It mitigates greenhouse gas emissions by sequestering carbon in biochar and displacing fossil fuels with biofuels.
- It promotes circular economy principles by converting waste materials into valuable resources.

Applications
Pyrolysis technology finds applications in various sectors, including:
Waste Management
Treating municipal solid waste, plastic waste, and hazardous materials.
Biomass Conversion
Converting agricultural residues and forestry waste into biofuels and biochar.
Tyre Recycling
Recycling used tires to recover valuable materials.
Oil Industry
Upgrading heavy oils and converting feedstock into valuable products.



